CDB in Action
SUSTAIN
The Socially Conscious pillar prioritises financial inclusion for underbanked and unbanked demographics and community impact through an ethos of corporate volunteerism and meaningful community projects.
Reducing our carbon footprint
GRI 3-3, 305-4, 305-5

CDB has been certified as a “Carbon Neutral Business Entity” by Climate Smart Initiatives (Pvt) Ltd. The collaboration has facilitated knowledge sharing and support, enabling CDB to provide customers and the community with unique environmentally conscious solutions. As a responsible corporate citizen, a reliable financier, and a trusted employer, CDB continues to exert a positive influence over stakeholders, demonstrating its commitment to sustainability in the various roles within society.
Since 2016, CDB has actively measured its carbon footprint and has partnered with an external organisation, the Sri Lanka Climate Fund, to undertake this crucial task. As part of its ongoing commitment, the Company intend to transparently disclose its carbon footprint information. CDB firmly upholds its goal of attaining net-zero status by 2030, demonstrating its dedication to mitigating environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices.
Steps taken to achieve net zero status

Timeline toward full net zero status by 2030:
- 2015 - CDB embarked on the carbon footprint calculation journey.
- 2015/16 - Was recognised as the first ISO 14064-1 carbon-verified financial institution in South Asia by the Sri Lanka Carbon Fund.
- 2022/23 - Became a Carbon verified company for the 8th consecutive year.
By pledging its commitment to the UNFCCC Climate Neutral Now initiative, CDB join a worldwide network of organisations dedicated to achieving climate neutrality by the latter half of the 21st century. This pledge exemplifies the Company’s determination to minimise emissions and expedite the transition toward a carbon-neutral future on a global scale. As part of this commitment, CDB diligently measures and reports its greenhouse gas emissions over a specified timeframe, striving to reduce them significantly.
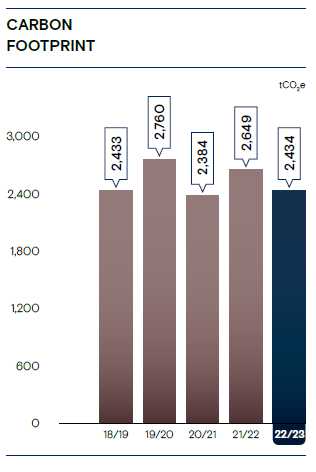
Carbon reporting enables CDB to analyse, assess and manage all resulting greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions emanating from its business operations, track the progress of energy reduction schemes, and optimise its energy consumption. CDB’s total carbon emission for FY 2022/23 was 2,434 tCO2e compared to 2,649 tCO2e in the previous year.

 Direct emissions
Direct emissions
GRI 305-1
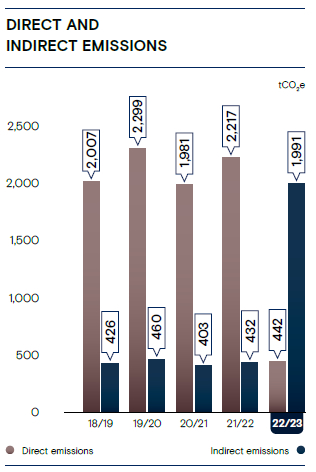
Direct emissions occur from sources that are controllable by our Organisation and they made the least contribution of 441.64 (tCO2e) which amounts to 18.15% of the total emissions. These emissions include emissions from onsite diesel generators, refrigerant leakage, fire extinguishers, Company-owned vehicles fuel paid by the Company and employee transport paid by the Company.
Total distribution of carbon footprint by Direct sources (2022/23)
 Indirect emissions
Indirect emissions
GRI 305-2
Indirect emissions occur from sources owned or controlled by another entity and make the highest contribution to our total GHG emissions, compared to direct emissions. The highest contributor to indirect emissions is electricity generated from the grid. We have implemented measures to save energy across our Company to reduce GHG emissions.
Total distribution of carbon footprint by Indirect sources (2022/23)
Achieving efficiency in energy management
GRI 302-1, 302-2, 302-4, 302-5

Energy management plays a crucial role in ensuring sustainable and efficient use of resources. It helps optimise energy consumption, reduce costs, and minimise environmental impact. By implementing effective energy management practices, organisations and individuals can identify areas of energy wastage, implement energy-saving measures, and adopt renewable energy sources. This not only lowers energy bills but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions, conserves natural resources, and contributes to mitigating climate change. Energy management is essential for promoting sustainability, resilience, and a greener future for our planet.
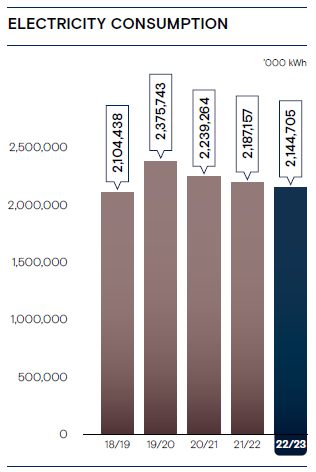
Accordingly, CDB continues to monitor and report the amount of energy produced, purchased and consumed based on the energy source. The energy consumption for FY 2022/23 was 2.14 Mn. kWh. which is 2.07% less than the previous year’s recorded figure. The following measures have helped to reduce its energy consumption:
- Reducing energy consumption by collaborating with suppliers and peers.
- Setting energy efficiency standards.
- Adopting cost-effective technologies.
- Promoting energy efficiency through regular energy audits.
CDB is also focused on:
- Monitoring and documenting energy usage, as well as measuring reductions and intensity, with a focus on decreasing energy consumption within our operations. This includes the mandatory utilisation of efficient lighting and electrical appliances, assessed annually during the CDB GHG emission analysis process.
- Promoting employee awareness regarding energy conservation and enhancing energy efficiency in their households by engaging in competitions.
- Implementing the Green branch concept, which involves
incorporating sustainable practices and technologies, such as installing solar power systems across our branch network. - Integrating the support and advancement of household renewable energy solutions, and promotion of renewable energy consumption into our medium-term business strategy.
Effective water management
GRI 303-1, 303-2, 303-5

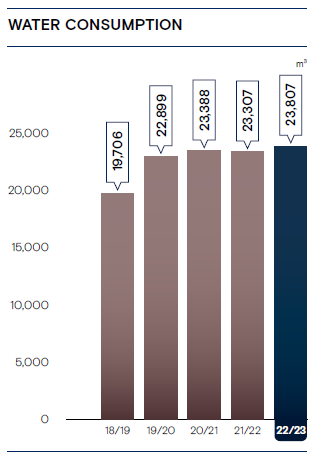
Effective water management is crucial due to its significance in sustaining life, ecosystems, and economic activities. It ensures the availability of clean water for drinking, sanitation, and agriculture while preventing water scarcity and pollution. Efficient water management practices promote environmental sustainability, and preserve aquatic habitats, groundwater tables, and aquifers. Additionally, it helps mitigate the impacts of climate change, reduces conflicts over water resources, and enhances overall resilience to water-related challenges.
CDB has adopted the following measures to manage its water consumption while respecting its team members’ right to safe drinking water and sanitation through availability, accessibility, acceptability, and quality of water. We have been educating our team members on how to segregate waste for recycling, and we are trying to extend this project to the branches, starting from Colombo, Western Province and then to island wide branch network. We are also engaging our suppliers on-board in this regard.
- Improving water performance, by promoting reuse through a rainwater harvesting system for gardening.
- Sharing smart solutions with peers and creating awareness of water conservation among team members.
- Organising competitions to commemorate the World Water
Day to build team member awareness. - Providing safe and hygienic gender-separate washroom facilities to team members.
- Responsible for disposal of sanitary products and medical waste, storage of cleaning equipment, and providing sanitation and hygiene training to team members.
Waste Management
GRI 301-1, 301-2, 306-1, 306-2

Effective waste management is crucial for addressing environmental, social, and health risks. It minimises pollution, conserves resources, and protects ecosystems. Proper management of food, paper, plastic, and e-waste reduces landfill burden, greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and pollution. It also prevents hazardous materials from entering the groundwater and contaminating the environment. Prioritising comprehensive, segregated waste management ensures a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future.
For efficient management and disposal of all forms of waste materials, CDB maintains waste disposal records at the head office. The team members are educated on reducing waste in general, including food waste and paper waste to inculcate a mindset of responsible waste management, which is crucial to reducing our environmental footprint. The following measures were adopted to efficiently manage waste:
- Implemented the CDB Advance Recycling Corner in the head office in commemoration of Global Recycling Day 2022, to encourage responsible disposal of paper, plastic, and electronic waste by our team members. We plan to replicate this recycling corner across our branch network.
- Upholding the commitment of all team members to the CDB Single-Use Plastic-Free Pledge, initiated during the 2019/20 World Environment Day. As the next phase, CDB is actively exploring alternatives to plastic items used within the Organisation.
- Established CDB e-waste and paper waste recycling programs to instil a sense of responsibility in waste management within its operations. These programmes aim to assess and prevent any actual or potential negative impacts on soil, wildlife, ecosystems, and the food chain.
- Implemented a waste segregation system with colour-coded bins and maintained comprehensive waste disposal records at our head office to enhance waste management practices.
- Initiated a pen recycling programme to collect and recycle used pens across its branch network.
- Encourage team members to minimise food waste and actively contribute to a sustainable environment.
- Enhanced environmental literacy and fostered grassroots engagement by sharing e-flyers and videos on sustainable development goals among all team members.
Waste disposal for FY 2022/23
GRI 306-3, 306-4, 306-5

Biodiversity sustains the resilience and productivity of ecosystems, supporting vital processes such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control.
Protecting and conserving biodiversity
GRI 3-3, 304-3

Protecting and conserving biodiversity is vital for the well-being of ecosystems, plant and animal life, and the sustainable management of natural resources. Biodiversity sustains the resilience and productivity of ecosystems, supporting vital processes such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control. Preserving biodiversity safeguards endangered species and maintains the balance of ecosystems. Additionally, it ensures the availability of diverse genetic resources for medicine, agriculture, and other industries. By valuing and protecting biodiversity, we secure the benefits it provides to ecosystems, plant and animal life, and the sustainable utilisation of natural resources.
By valuing and protecting biodiversity, we secure the benefits it provides to ecosystems, plant and animal life, and the sustainable utilisation of natural resources.
The LIFE Project – Restoring degraded land
GRI 304-1, 304-2, 304-3
By restoring degraded areas, we can combat desertification, soil erosion, and loss of biodiversity. We can also improve soil fertility, enhance water retention, and promote the growth of vegetation while contributing to climate change mitigation by sequestering carbon dioxide. Furthermore, it supports sustainable agriculture, boosts local economies, and provides ecological benefits such as habitat restoration and water purification. Restoring degraded land is essential for achieving environmental sustainability and ensuring the well-being of both ecosystems and communities.
In this regard, CDB has commenced a landmark public-private initiative to restore one hectare of degraded land, which will form the basis of further projects of this nature.
- Area: Halgahawala, Opatha, adjacent to Kanneliya rainforest.
- Period: The project duration spans five years, with four years already completed. CDB is poised to extend this project for an additional five years, with the potential for further extensions to maximise value addition and reap additional benefits.
- Aim: Restore a 10-ha block of degraded rainforest land in the Kanneliya forest reserve. This will be a model for the restoration of degraded forest landscapes in the wet zone of Sri Lanka. It aims to develop a biodiversity credit accrual system on par with international standards. It would enable biodiversity conservation project owners to generate accruable non-carbon credits.
- Partners: Biodiversity Sri Lanka (BSL), the Forest Department, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Sri Lanka together with 11 private sector partners. CDB is in the process of finalising the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to extend this project for another five years, with provisions for further extensions if deemed necessary.
- Achievements and Impacts:
- Two additional hectares of degraded land area were annexed to the existing site, and restoration activities were initiated.
- Implemented an intensive restoration approach by employing various adaptive methodologies, including selectively removing Kekilla vegetation, enlarging planting pits, managing on-site nurseries, utilising organic fertilisers, implementing soil conservation and improvement techniques, and adopting plant protection measures.
- Five monitoring visits were carried out during the reporting period.
- Action taken to finalise the
Forest Ecosystem Restoration:
Field Verification Standard with NEPCon – an international accreditation agency
The Life to Our Mangroves project
GRI 304-1, 304-2, 304-3
Mangrove conservation and restoration are of immense importance, as mangroves provide critical habitats for a diverse range of species, support coastal ecosystems and protect against erosion, storm surges, and tsunamis. They act as carbon sinks, mitigating climate change. Mangroves also sustain local economies through fisheries, ecotourism, and natural products. Conserving and restoring mangroves enhances coastal resilience, conserves biodiversity, and contributes to climate change adaptation. Preserving and restoring mangrove ecosystems is vital for the well-being of coastal communities and the overall health of our planet.
CDB is currently engaged in a venture that aims to introduce a Nature-based Solution (NbS) in the form of a Mangrove Restoration Project, offering a range of environmental and socioeconomic advantages. By implementing this intervention, the resilience of the mangrove ecosystem will be enhanced, promoting its ability to regenerate and provide essential ecosystem services. Simultaneously, the project will contribute to the socioeconomic progress of local communities. The primary focus will be the conservation of 25 hectares of land within the Anawilundawa wetland sanctuary, a significant RAMSAR wetland site among the six identified.
- Aim: The objective is to strengthen the resilience of identified mangroves, and the benefits they provide to the ecosystem, while highlighting the significance of mangrove restoration as a nature-based solution for mitigating the effects of climate change and addressing socio-economic development challenges. The project also seeks to promote community readiness and build partnerships to reduce Sri Lanka’s vulnerability to climate change.
- Partners: In collaboration with Biodiversity Sri Lanka, the Department of Wildlife Conservation and ten corporates.
- Key activities: This is a five-year project that will focus on the following key activities:
- Baseline survey and stakeholder mapping.
- Planning of restoration processes, procurement and allocation of resources, ground implementation of ecological restoration process including setting up mangrove nurseries.
- The ground preparation levels and planting activities have already been commenced.
- Formulating monitoring criteria and record-keeping and reporting mechanisms.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation of data gathered periodically.
The Ittapana Mangrove Conservation project
GRI 304-1, 304-2, 304-3
- Partnership: with the Centre for Sustainability of the University of Sri Jayewardenepura.
- Area: Conserves 10 acres of Ittapana – Horawala mangrove forest which is one of the most threatened landscapes in Sri Lanka. Establish a mangrove research centre for mangrove ecosystem studies.
- Aim: Establish a demonstrative model for sustainable mangrove management adaptable to other mangrove ecosystem conservation in Sri Lanka.
- Key activities: Two-year project that will focus on the following key activities in subsequent years:
- Set up a Mangrove Education and Research Centre with the aim of enhancing understanding and knowledge about the Mangrove Ecosystem.
- Eliminate invasive species present on the site.
- Develop an open mangrove arboretum comprising a diverse range of native, threatened, and rare mangrove and mangrove-associated plant species that can grow freely.
- Establish a dedicated mangrove plant nursery to propagate and cultivate mangrove plants for restoration and conservation.
Reducing our carbon footprint
As a responsible financial services organisation, with a minimal carbon footprint, CDB strives to achieve
net-zero status to fulfil its environmental responsibilities. By reducing carbon emissions, the Company is able to demonstrate its commitment to sustainability, mitigate climate change risks, and align with evolving customer expectations. The net-zero status will also enhance its reputation, attracting environmentally conscious clients and employees, and contributing to a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
Investments in environmental initiatives in 2022/23
| Description | 2022/23 Rs. Mn. |
| Biodiversity conservation and ecosystem restoration | 2.35 |
| Education and engagement | 2.82 |
| Carbon footprint management | 2.05 |
| Training | 0.65 |
| Total | 7.87 |
Future outlook
We have aligned our business strategy into the sustainability agenda, complemented by the tech disruption we are embarked on. We plan to improve our environmental and social risk management framework to further strengthen our commitment.
We believe awareness and education as the best way to change action. We will continue to invest in awareness campaigns focusing on team members, customers and society at large. We will expand collaborations with other entities and Government bodies to foster sustainability.
Furthermore, CDB is working on establishing a carbon credit accrual programme to account for carbon credits generated by its projects, as the current system lacks international certification. To advance its net-zero agenda, the Company will focus on increasing EV conversions and expanding charging infrastructure, setting measurable KPIs. CDB aims to drive demand for conversions by introducing an affordable product and offering special benefits for hybrid vehicles. These efforts align with its commitment to sustainability and reducing carbon emissions.
These efforts will contribute to a more sustainable future, align with global sustainability goals, and demonstrate the Company’s commitment to responsible environmental practices. By focusing on these areas, CDB aims to enhance its reputation, attract environmentally conscious customers, and position itself as a leader in sustainable finance.





